Groundbreaking Gene Therapy
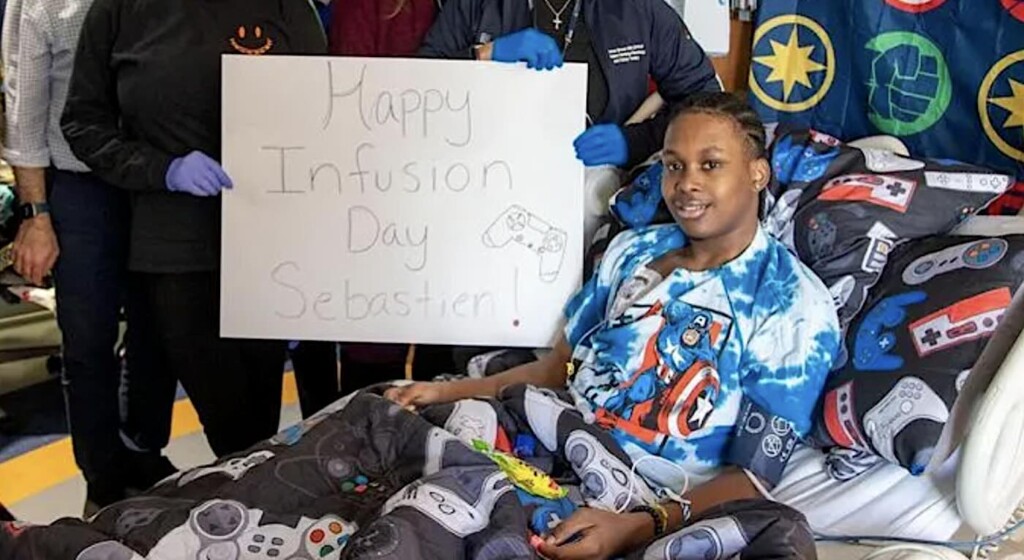
A New York hospital has announced a groundbreaking milestone: a patient has been cured of sickle cell anemia using a cutting-edge genetic therapy. Cohen Children’s Medical Center reports that 21-year-old Sebastien Beauzile is the first New Yorker to receive Lyfgenia, a treatment developed by Bluebird Bio. Since undergoing the therapy in December 2024, Beauzile has been free from the disease’s debilitating symptoms, including skin ulcers, joint pain, and chest pain—marking what he calls his “new birthday.”
Sickle cell disease is caused by a genetic mutation that deforms red blood cells, impairing their ability to transport oxygen. Until now, bone marrow transplants were the only potential cure. Lyfgenia changes that equation by introducing healthy adult hemoglobin into the patient’s bone marrow, allowing the body to generate normal red blood cells. Dr. Jeffrey Lipton, director of pediatric hematology at Cohen Children’s, called the therapy “a fix” and suggested it could one day replace bone marrow transplants as the standard of care.
Gene therapy is rapidly transforming the landscape of sickle cell treatment. In a separate case, 20-year-old Brandon Baptiste appears to have been cured using base editing, a novel approach that doesn’t rely on CRISPR. After participating in an experimental trial, Baptiste has returned to an active lifestyle, including regular exercise. These breakthroughs signal a promising shift in the fight against sickle cell anemia, offering hope that more patients will soon have access to lasting, life-changing solutions.