Carbon Dioxide Bricks
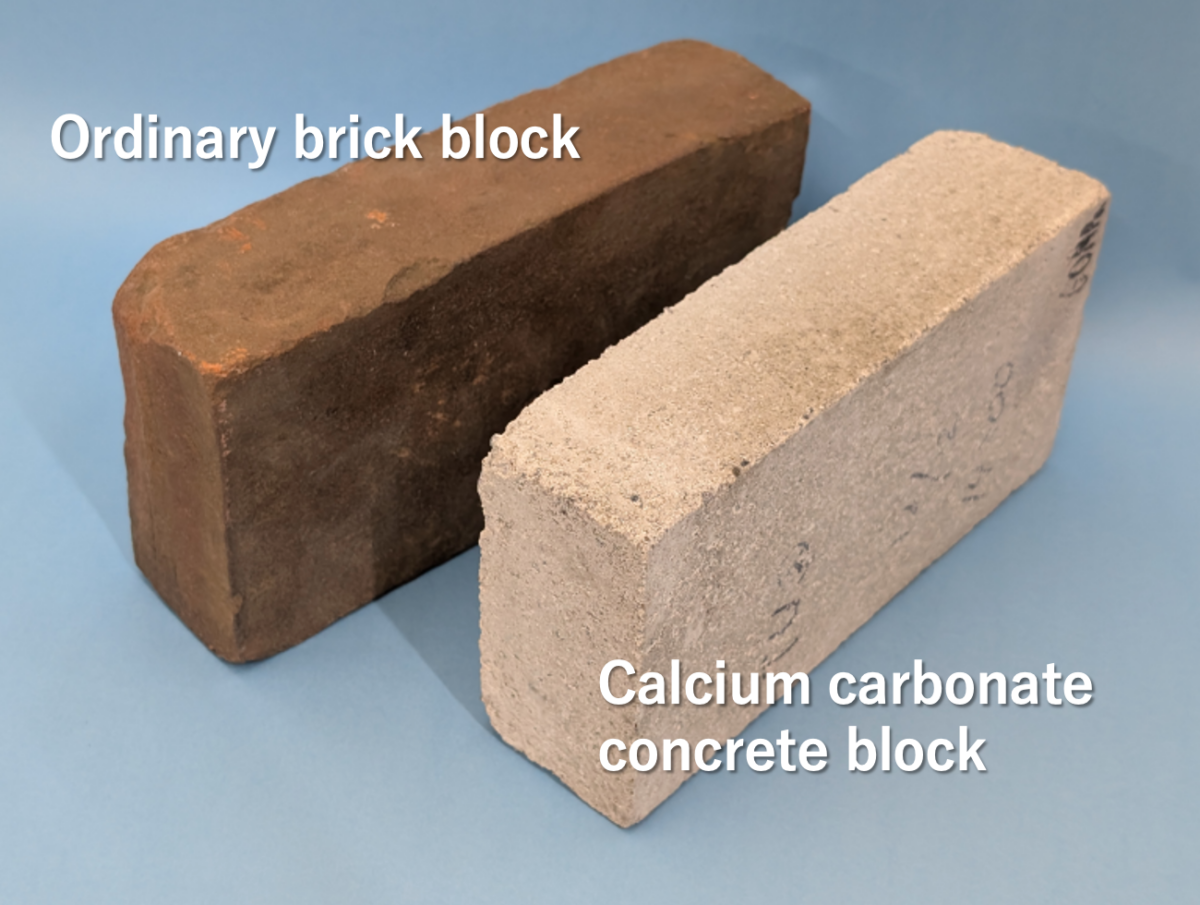
A team of researchers from the University of Tokyo, in collaboration with Tokyo University of Science and Taiheiyo Cement Corporation, has developed a groundbreaking method to recycle concrete from a demolished school building and carbon dioxide from the air into new bricks strong enough to be used in house construction.
The process involves pulverizing the old concrete into a fine powder, which is then mixed with captured carbon dioxide. The mixture is then pressurized in layers using molds and heated to form solid concrete blocks. This innovative technique not only makes it easier and more feasible to recycle old materials but also traps carbon dioxide, reducing environmental impact. Moreover, these “refreshed” blocks can be reprocessed into new blocks if the buildings are later demolished.
The researchers explain that the recycled concrete blocks undergo a carbonation process over three months, which typically takes years in natural conditions. During this process, compounds like portlandite and calcium silicate hydrate in the concrete are transformed into calcium carbonate, strengthening the material over time. To expedite this process while ensuring the recycled blocks remain strong, the team pressurizes the carbonated powder with a calcium bicarbonate solution, then dries it to solidify the blocks. This recent experiment builds on previous efforts by layering and compacting the material inside molds, resulting in denser and stronger blocks compared to earlier methods.
This research is part of the C4S project (Calcium Carbonate Circulation System for Construction), led by Professor Takafumi Noguchi, with material development headed by Professor Ippei Maruyama. The project’s goal is to create durable recycled concrete blocks, known as “calcium carbonate concrete,” by incorporating carbon dioxide from the air or industrial exhaust. “As part of the C4S project, we intend to construct a real two-story house by 2030,” says Professor Maruyama. “In the coming years, we plan to scale up to a pilot plant, improve production efficiency, and develop larger building elements as we work towards commercializing this material.”